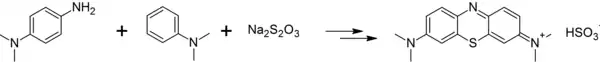Dimethyl-4-phenylenediamine
Dimethyl-4-phenylenediamine is an amine. It has been used as an accelerator for the vulcanization of rubber.[2] It can be used in oxidase tests.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N1,N1-Dimethylbenzene-1,4-diamine | |
| Other names
p-Aminodimethylaniline; N,N-Dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine; 4-(Dimethylamino)aniline; p-Amino-N,N-dimethylaniline; p-(Dimethylamino)aniline; DMPPDA; Dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine; 4-Amino-N,N-dimethylaniline; p-Dimethylaminophenylamine; DMPD | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.552 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H12N2 | |
| Molar mass | 136.198 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Reddish-violet crystals[1] |
| Melting point | 53 °C (127 °F; 326 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 262 °C (504 °F; 535 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Synthesis
Dimethyl-4-phenylenediamine is made by the nitrosylation of dimethylaniline followed by reduction.
Applications
Dimethyl-4-phenylenediamine can be converted to methylene blue by reaction with dimethylaniline and sodium thiosulfate in several steps:[3]
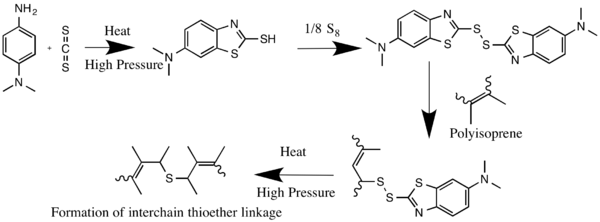
It is used as accelerator for the vulcanization of rubber, being first converted to the corresponding mercaptobenzothiazole.
References
- Merck Index, 11th Edition, 3242
- Geer, W. C.; Bedford, C. W. (January 24, 1925). "The History of Organic Accelerators in the Rubber Industry". Industrial and Engineering Chemistry. 17 (4): 393–396. doi:10.1021/ie50184a021.
- Horst Berneth (2012). "Azine Dyes". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_213.pub3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.