ܐܫܘܪ
Assyrian Neo-Aramaic
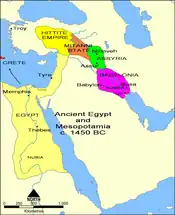
ܒܹܝܬ ܢܲܗܪ̈ܝܼܢ ܡܸܩܕܲܪ 1450 ܩܡܕ

ܐܵܬܵܐ ܕܐܵܫܘܿܪ
Alternative forms
- ܐܵܬܘܿܪ (ātor)
Etymology
Modern Learned borrowing from Aramaic אֲשׁוּר (ˀăšūr), from Akkadian 𒀸𒋩𒆠 (Aššūr, “Ashur”) the original capital named after the chief deity of that city. Doublet of ܐܵܬ݂ܘܿܪ (āṯor, “Assyria”).
Pronunciation
- IPA(key): [aːʃʊr]
Proper noun
ܐܵܫܘܿܪ • (āšor) f
- Assyria: A Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation-state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia (present-day northern Iraq), that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history.
- Assur: An ancient city on the western bank of the Tigris River, originally ruled by its tutelary deity from which the natives took their name, as did the entire nation of Assyria.
Proper noun
ܐܵܫܘܿܪ • (āšor) m
Derived terms
- ܐܵܫܘܿܪܵܝܵܐ (āšoraya, “Assyrian”)
Related terms
- ܐܵܬܘܿܪ (ātor, “Assyria”)
- ܐܵܬܘܿܪܵܝܵܐ (ātoraya, “Assyrian”)
This article is issued from Wiktionary. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.