1-Butyne
1-Butyne is an organic compound with the chemical formula HC2CH2CH3.
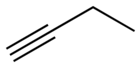 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
But-1-yne | |
| Other names
Ethylacetylene Ethylethyne, UN 2452 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.139 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2452 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties[1] | |
| C4H6 | |
| Molar mass | 54.091 g/mol |
| Density | 0.6783 g cm−3[1] |
| Melting point | −125.7 °C (−194.3 °F; 147.5 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 8.08 °C (46.54 °F; 281.23 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H220, H280 | |
| P210, P377, P381, P403 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
It is a colorless combustible gas.[1] 1-Butyne participates in reactions typical for terminal alkynes, such as alkyne metathesis,[2] hydrogenation, condensation with formaldehyde. Based on its heat of combustion, it is slightly more stable than its isomer 2-butyne.[3]
See also
References
- Lide, David R. (2008). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 89th Edition. CRC Press. pp. 3–84. ISBN 978-0-8493-0488-0.
- Zhang, Wei; Kraft, Stefan; Moore, Jeffrey S. (2004). "Highly Active Trialkoxymolybdenum(VI) Alkylidyne Catalysts Synthesized by a Reductive Recycle Strategy". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 126 (1): 329–335. doi:10.1021/ja0379868. PMID 14709099.
- Prosen, E.J.; Maron, F.W.; Rossini, F.D. (1951). "Heats of combustion, formation, and insomerization of ten C4 hydrocarbons". Journal of Research of the National Bureau of Standards. 46 (2): 106. doi:10.6028/jres.046.015.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.