主
| ||||||||
Translingual
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Stroke order (Japan) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
Han character
主 (Kangxi radical 3, 丶+4, 5 strokes, cangjie input 卜土 (YG), four-corner 00104, composition ⿱丶王 or ⿱亠土)
Derived characters
References
- KangXi: page 80, character 20
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 100
- Dae Jaweon: page 163, character 1
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 1, page 44, character 3
- Unihan data for U+4E3B
Chinese
| simp. and trad. |
主 | |
|---|---|---|
| alternative forms | 丶 宔 | |
Glyph origin
| Historical forms of the character 主 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | ||||||||
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Small seal script | ||||||||
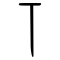 |
 |
 | ||||||||
| ||||||||||
|
References: Mostly from Richard Sears' Chinese Etymology site (authorisation),
| ||||||||||
Pictogram (象形) : A picture of a lamp or a torch with a flame at the top.
Original form of 炷. Current meaning acquired by sound loan.
Etymology
Unclear. Compare Tibetan ཇོ་བོ (jo bo, “elder brother, nobleman, lord”), Tibetan ཇོ་མོ (jo mo, “mistress, lady, goddess”), Tibetan ཐུ། (thu, “chief”), Proto-Monic *(d)ndooʔ (“to teach, to instruct; headman”), and Thai โจก (jòok, “leader, chief”) (Schuessler, 2007)
Pronunciation 1
Definitions
主
- owner; master
- host
- (archaic, honorific) you (honorific second-person pronoun addressing a "senior official" [大夫] or his spouse)
- 季康子問于共父文伯之母曰:「主亦有以語肥也。」對曰:「吾能老而已,何以語子。」康子曰:「雖然,肥愿有聞于主。」 [Classical Chinese, trad.]
- From: Guoyu, circa 4th century BCE
- Jì Kāngzǐ wèn yú Gōngfǔ Wénbó zhī mǔ yuē: “Zhǔ yì yǒu yǐ yù Féi yě.” Duìyuē: “Wú néng lǎo éryǐ, héyǐ yù zǐ.” Kāngzǐ yuē: “Suīrán, Féi yuàn yǒu wén yú zhǔ.” [Pinyin]
- Ji Kangzi (Fei) consulted the mother of Gongfu Wenbo: "Would you, madame, have something to instruct me?" "I am only good at growing old. What else can I tell you?" came her reply. "Nevertheless, I, Fei, do want to hear something from you," said Kangzi.
季康子问于共父文伯之母曰:“主亦有以语肥也。”对曰:“吾能老而已,何以语子。”康子曰:“虽然,肥愿有闻于主。” [Classical Chinese, simp.]
- (Christianity, Islam) Lord
- emperor
- (colloquial, derogatory) person of a specified type
- agent; agency
- 夫民,神之主也。 [Classical Chinese, trad. and simp.]
- From: Commentary of Zuo, c. 4th century BCE
- Fú mín, shén zhī zhǔ yě. [Pinyin]
- The people are the agent of divine spirits.
- party; entity
- 事主 ― shìzhǔ ― party (in a dispute, especially the one bringing forth the dispute)
- main; primary; principal; major
- to be in charge; to lead; to command
- 主事 ― zhǔshì ― to be in charge
- to indicate; to signify
- (grammar) Short for 主語/主语 (zhǔyǔ).
- (historical) Short for 公主 (gōngzhǔ).
- a surname
Compounds
|
|
|
Descendants
Others:
Pronunciation 2
References
- “主”, in 漢語多功能字庫 (Multi-function Chinese Character Database), 香港中文大學 (the Chinese University of Hong Kong), 2014–
Japanese
| Shinjitai | 主 | 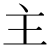 |
| Kyūjitai [1][2][3] |
主󠄁 主+ 󠄁?(Adobe-Japan1) |
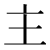 |
| 主󠄃 主+ 󠄃?(Hanyo-Denshi) (Moji_Joho) | ||
| The displayed kanji may be different from the image due to your environment. See here for details. | ||
Readings
Compounds
Etymology 1
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 主 |
| しゅ Grade: 3 |
| on’yomi |
Synonyms
- 主人 (shujin)
Etymology 2
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 主 |
| ぬし Grade: 3 |
| kun’yomi |
| For pronunciation and definitions of 主 – see the following entry. | ||
| ||
| (This term, 主, is an alternative spelling of the above term.) |
Etymology 3
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 主 |
| おも Grade: 3 |
| kun’yomi |
| For pronunciation and definitions of 主 – see the following entry. | ||
| ||
| (This term, 主, is an alternative spelling of the above term.) |
Etymology 4
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 主 |
| あるじ Grade: 3 |
| kun’yomi |
| For pronunciation and definitions of 主 – see the following entry. | ||
| ||
| (This term, 主, is an alternative spelling of the above term.) |
References
- 白川静 (Shirakawa Shizuka) (2014), “主”, in 字通 普及版 (Jitsū fukyūban, “Jitsū trade edition”) (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Heibonsha, →ISBN
- 1914, 漢和大辭書 (Kanwa Dai Jisho, “The Great Kanji-Japanese Dictionary”) (in Japanese), page 62 (paper), page 81 (digital), Tōkyō: 興文社 (Kōbunsha)
- 1927, 新漢和辭典 (Shin Kanwa Jiten, “The New Kanji-Japanese Dictionary”) (in Japanese), page 56 (paper), page 40 (digital), Ōsaka: 松雲堂 (Shōundō)
- 2006, 大辞林 (Daijirin), Third Edition (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Sanseidō, →ISBN
Korean
Etymology
From Middle Chinese 主 (MC t͡ɕɨoX). Recorded as Middle Korean 쥬〮 (cyú) (Yale: cyu) in Hunmong Jahoe (訓蒙字會 / 훈몽자회), 1527.
Compounds
References
- Naver Hanja Dictionary: 主
- 국제퇴계학회 대구경북지부 (國際退溪學會 大邱慶北支部) (2007). Digital Hanja Dictionary, 전자사전/電子字典.
Vietnamese
Han character
Usage notes
- Despite being a non-Sino-Vietnamese reading, chúa is still used as Sino-Vietnamese in a few compounds such as Chúa nhật, công chúa, quận chúa, lãnh chúa, Thiên Chúa.







