戎
See also: 戒
| ||||||||
Translingual
Han character
戎 (Kangxi radical 62, 戈+2, 6 strokes, cangjie input 戈十 (IJ), four-corner 53400, composition ⿹戈𠂇(GHTJK) or ⿻戊一(V))
Derived characters
References
- KangXi: page 411, character 8
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 11539
- Dae Jaweon: page 752, character 12
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 2, page 1397, character 8
- Unihan data for U+620E
Chinese
| simp. and trad. |
戎 | |
|---|---|---|
| alternative forms | 𢦦 ancient form 𢍻 historical form found in 漢孔宙碑 𫻳 ancient form in Bronze inscription | |
Glyph origin
| Historical forms of the character 戎 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) |
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts |
 |
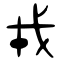 |
 |
 |
Characters in the same phonetic series (戎) (Zhengzhang, 2003)
Ideogrammic compound (會意) : 盾 (“shield”) + 戈 (“halberd; weapons”) – weaponry, arms.
Etymology
- “you”
- From Proto-Sino-Tibetan *na-ŋ (“you”).
- “ancient tribe”
- Unknown. Goldin (2011) proposes that 戎 (róng) was a pejorative "pseudo-ethnonym" meaning "bellicose".
Pronunciation
Definitions
戎
- (literary) arms, armaments
- 是月也,天子乃教於田獵,以習五戎,班馬政。 [Classical Chinese, trad.]
- From: The Book of Rites, c. 4th – 2nd century BCE
- Shì yuè yě, tiānzǐ nǎi jiào yú tiánliè, yǐ xí wǔróng, bān mǎ zhèng. [Pinyin]
- In this month the son of Heaven, by means of hunting, teaches how to use the five weapons of war, and the rules for the management of horses.
是月也,天子乃教于田猎,以习五戎,班马政。 [Classical Chinese, simp.]
- (literary) army; military affairs
- 國之大事,在祀與戎。 [Classical Chinese, trad.]
- From: Commentary of Zuo, c. 4th century BCE, translated based on James Legge's version
- Guó zhī dàshì, zài sì yǔ róng. [Pinyin]
- The great affairs of the state are sacrifice and warfare.
国之大事,在祀与戎。 [Classical Chinese, simp.]
- (obsolete) you
- 戎雖小子,而式弘大。 [Pre-Classical Chinese, trad.]
- From: The Classic of Poetry, c. 11th – 7th centuries BCE, translated based on James Legge's version
- Róng suī xiǎozǐ, ér shì hóngdà. [Pinyin]
- Though you may be [but as] little children, your work is vast and great.
戎虽小子,而式弘大。 [Pre-Classical Chinese, simp.]
- (historical) a general term for ethnic groups in the west of China
- See also: 西戎
- 是以秦用戎人由余而霸中國,齊用越人蒙而彊威、宣。 [Classical Chinese, trad.]
- From: The Records of the Grand Historian, by Sima Qian, c. 91 BCE
- Shìyǐ Qín yòng Róngrén Yóuyú ér bà Zhōngguó, Qí yòng Yuèrén Méng ér qiáng Wēi, Xuān. [Pinyin]
- So Qin used the Rong man Youyu and established hegemony over the central states, Qi used the Yue man Meng and strengthened (kings) Wei and Xuan.
是以秦用戎人由余而霸中国,齐用越人蒙而强威、宣。 [Classical Chinese, simp.]
- a surname
Compounds
References
- “戎”, in 漢語多功能字庫 (Multi-function Chinese Character Database), 香港中文大學 (the Chinese University of Hong Kong), 2014–
Japanese
Korean
Vietnamese
This article is issued from Wiktionary. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.