卒
| ||||||||
Translingual
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
Han character
卒 (Kangxi radical 24, 十+6, 8 strokes, cangjie input 卜人人十 (YOOJ), four-corner 00408, composition ⿱𠅃十)
Derived characters
Descendants
References
- KangXi: page 156, character 28
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 2740
- Dae Jaweon: page 356, character 19
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 1, page 63, character 2
- Unihan data for U+5352
Chinese
| simp. and trad. |
卒 | |
|---|---|---|
| 2nd round simp. | 卆 | |
| alternative forms | ||
Glyph origin
| Historical forms of the character 卒 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Warring States | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) | |||
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Chu slip and silk script | Qin slip script | Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts |
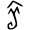 |
 |
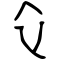 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Characters in the same phonetic series (卒) (Zhengzhang, 2003)
| Old Chinese | |
|---|---|
| 晬 | *ʔsuːds |
| 祽 | *ʔsuːds |
| 綷 | *ʔsuːds |
| 淬 | *sʰuːds |
| 啐 | *sʰuːds, *suːds, *sʰroːds, *ʔsud |
| 倅 | *sʰuːds, *ʔsuːd |
| 焠 | *sʰuːds |
| 碎 | *suːds |
| 誶 | *suːds, *suds, *zud |
| 濢 | *ʔslulʔ, *sʰluds |
| 噿 | *ʔslulʔ |
| 臎 | *ʔslulʔ, *sʰluds |
| 醉 | *ʔsuds |
| 翠 | *sʰuds |
| 悴 | *zuds |
| 萃 | *zuds |
| 瘁 | *zuds |
| 顇 | *zuds |
| 粹 | *suds |
| 睟 | *suds |
| 賥 | *suds |
| 卒 | *ʔsuːd, *sʰuːd, *ʔsud |
| 稡 | *ʔsuːd |
| 猝 | *sʰuːd |
| 椊 | *zuːd |
| 捽 | *zuːd, *zud |
| 崪 | *zuːd |
| 窣 | *suːd |
| 崒 | *zud |
| 踤 | *zud |
| 錊 | *ʔsuːɡ |
There were 5 forms of 卒 in Shang oracle bone script (Qiu, 1990; Xuan, 2012):
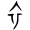 : same as 衣 (“clothes”) (> Western Zhou bronze script
: same as 衣 (“clothes”) (> Western Zhou bronze script  );
);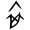 : a crisscross 衣 - a completed clothing;
: a crisscross 衣 - a completed clothing;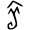 (卒): ideogrammic compound (會意) : 衣 (“clothes”) with a mark - a completed clothing to be folded (> Warring States bronze script
(卒): ideogrammic compound (會意) : 衣 (“clothes”) with a mark - a completed clothing to be folded (> Warring States bronze script  ; Chu slip and silk script
; Chu slip and silk script  );
); (𧙻): phono-semantic compound (形聲, OC *ʔsuːd, *sʰuːd, *ʔsud) : 衣 (“clothes”) + 聿 (OC *b·lud) (hand (又) holding a brush);
(𧙻): phono-semantic compound (形聲, OC *ʔsuːd, *sʰuːd, *ʔsud) : 衣 (“clothes”) + 聿 (OC *b·lud) (hand (又) holding a brush); ,
, : 𧙻 having 又 omitted.
: 𧙻 having 又 omitted.
The brush shape in form (5) was often placed upside down. Later the inverted brush shape was mistaken as 又 and then moved to the top as in Chu slip and silk script ![]() (𰠄) to avoid obscuration with 袁 (衣 + 又) (Xuan, 2012).
(𰠄) to avoid obscuration with 袁 (衣 + 又) (Xuan, 2012).
Etymology 1
From 遭 (OC *ʔsluː, “to meet”) + nominal suffix *-t (Schuessler, 2007).
Pronunciation
Synonyms
Dialectal synonyms of 卒子 (“xiangqi black pawn”) [map]
| Variety | Location | Words |
|---|---|---|
| Formal (Written Standard Chinese) | 卒子 | |
| Mandarin | Harbin | 卒兒 |
| Yantai (Muping) | 小卒兒, 卒 | |
| Jinan | 小卒兒 | |
| Luoyang | 卒子, 小卒 | |
| Xi'an | 卒子, 卒, 小卒 | |
| Yinchuan | 卒 | |
| Lanzhou | 卒子, 卒 | |
| Xining | 卒, 卒子, 尕卒兒 | |
| Ürümqi | 卒兒, 卒子, 卒娃子 | |
| Wuhan | 卒子, 卒 | |
| Guiyang | 卒子, 卒, 小卒子, 小卒 | |
| Liuzhou | 卒崽, 卒 | |
| Xuzhou | 小卒, 小卒子, 小卒兒, 卒頭子 | |
| Yangzhou | 卒子, 小卒子 | |
| Nanjing | 小卒, 卒子 | |
| Cantonese | Hong Kong | 卒 |
| Dongguan | 卒 | |
| Gan | Nanchang | 卒子, 卒 |
| Lichuan | 卒 | |
| Pingxiang | 卒仔, 卒 | |
| Hakka | Meixian | 卒 |
| Yudu | 卒子, 卒 | |
| Huizhou | Jixi | 卒 |
| Jin | Taiyuan | 卒子 |
| Xinzhou | 卒子, 黑卒子 | |
| Min Bei | Jian'ou | 卒仔 |
| Min Dong | Fuzhou | 卒, 卒囝 |
| Min Nan | Xiamen | 卒仔, 卒 |
| Quanzhou | 卒仔, 卒 | |
| Zhangzhou | 卒仔, 卒 | |
| Tainan | 卒仔 | |
| Leizhou | 卒囝 | |
| Haikou | 卒 | |
| Southern Pinghua | Nanning (Tingzi) | 卒崽, 卒 |
| Wu | Shanghai | 卒 |
| Shanghai (Chongming) | 卒 | |
| Suzhou | 卒 | |
| Danyang | 卒, 卒卒 | |
| Hangzhou | 卒卒兒 | |
| Ningbo | 卒格, 卒格爛眼 | |
| Wenzhou | 卒兒, 爛頭卒 | |
| Jinhua | 卒 | |
| Xiang | Changsha | 卒子, 卒 |
| Loudi | 卒子, 卒 | |
Coordinate terms
Compounds
Descendants
Etymology 2
(This etymology is missing or incomplete. Please add to it, or discuss it at the Etymology scriptorium. Particularly: “from ST *(t/d)u-n/t? Related to 瘁/悴, 酋, 傮, 造, 秋?”)
Pronunciation
Definitions
卒
Compounds
Pronunciation
Pronunciation
References
- “卒”, in 漢語多功能字庫 (Multi-function Chinese Character Database), 香港中文大學 (the Chinese University of Hong Kong), 2014–
- Dictionary of Chinese Character Variants (教育部異體字字典), A00437
Japanese
Readings
- Go-on: そち (sochi); しゅち (shuchi)
- Kan-on: そつ (sotsu, Jōyō); しゅつ (shutsu)
- Kun: にわかに (niwakani, 卒かに)←にはかに (nifakani, 卒かに, historical); おわる (owaru, 卒わる)←をはる (wofaru, 卒はる, historical); おえる (oeru, 卒える)←をへる (woferu, 卒へる, historical); ついに (tsuini, 卒に)←つひに (tufini, 卒に, historical)
Korean
Etymology 1
From Middle Chinese 卒 (MC t͡suət̚, “soldier”).
| Historical readings |
|---|
|
Pronunciation
- (SK Standard/Seoul) IPA(key): [t͡ɕo̞ɭ]
- Phonetic hangul: [졸]
Etymology 2
From Middle Chinese 卒 (MC t͡siuɪt̚, “finish”).
| Historical readings |
|---|
|
Pronunciation
- (SK Standard/Seoul) IPA(key): [t͡ɕo̞ɭ]
- Phonetic hangul: [졸]
Hanja
Compounds
Vietnamese
This article is issued from Wiktionary. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.