飲
| ||||||||
Translingual
Han character
飲 (Kangxi radical 184, 食+4, 13 strokes, cangjie input 人戈弓人 (OINO), four-corner 87782, composition ⿰飠欠)
Derived characters
- 𠿮 𡑨 𤀔 𥽁 𡼽 𫨜
References
- KangXi: page 1417, character 19
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 44063
- Dae Jaweon: page 1941, character 20
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 7, page 4445, character 7
- Unihan data for U+98F2
Chinese
Glyph origin
| Historical forms of the character 飲 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) |
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Transcribed ancient scripts |
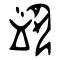 |
 |
 |
| Old Chinese | |
|---|---|
| 貪 | *kʰl'uːm |
| 嗿 | *l̥ʰuːmʔ |
| 僋 | *l̥ʰuːms, *luːms |
| 酓 | *qʰɯːm, *qlamʔ, *qlɯːms |
| 馠 | *qʰɯːm |
| 谽 | *qʰɯːm |
| 唅 | *qʰɯːm, *ɡɯːms |
| 含 | *ɡɯːm |
| 肣 | *ɡɯːm, *ɡɯːmʔ |
| 頷 | *ɡɯːm, *ɡɯːmʔ |
| 筨 | *ɡɯːm |
| 梒 | *ɡɯːm |
| 鋡 | *ɡɯːm |
| 莟 | *ɡɯːmʔ, *ɡɯːms |
| 琀 | *ɡɯːms |
| 浛 | *ɡɯːms |
| 盦 | *qɯːm, *qaːb |
| 韽 | *qɯːm, *qrɯːms |
| 玪 | *krɯːm |
| 妗 | *qʰrɯːm, *kʰjam, *qʰlɯːm, *ɡrɯms |
| 欦 | *qʰrɯːmʔ, *qʰram, *kʰlam, *kʰlamʔ, *qʰlɯːm |
| 黔 | *ɡram, *ɡrɯm |
| 鈐 | *ɡram |
| 鳹 | *ɡram |
| 雂 | *ɡram, *ɡrɯm |
| 念 | *nɯːms |
| 梣 | *sɡɯm, *sɡrɯm |
| 枔 | *sɢrɯm |
| 岑 | *sɡrɯm |
| 笒 | *sɡrɯm, *ɡrɯms |
| 涔 | *sɡrɯm |
| 侺 | *ɡjɯms |
| 今 | *krɯm |
| 黅 | *krɯm |
| 衿 | *krɯm |
| 衾 | *kʰrɯm |
| 坅 | *kʰrɯmʔ |
| 搇 | *kʰrɯms |
| 琴 | *ɡrɯm |
| 禽 | *ɡrɯm |
| 芩 | *ɡrɯm |
| 庈 | *ɡrɯm |
| 耹 | *ɡrɯm |
| 靲 | *ɡrɯm |
| 擒 | *ɡrɯm |
| 檎 | *ɡrɯm |
| 紟 | *ɡrɯms |
| 吟 | *ŋɡrɯm, *ŋɡrɯms |
| 訡 | *ŋɡrɯm |
| 廞 | *qʰrɯm, *qʰrɯmʔ |
| 陰 | *qrɯm |
| 霠 | |
| 飲 | *qrɯmʔ, *qrɯms |
| 蔭 | *qrɯms |
| 廕 | *qrɯms |
| 矜 | *ɡrɯn, *ɡɯn, *kɯŋ |
In the oracle bone script, it was an ideogrammic compound (會意) : 酉 (“bottle (of alcoholic beverages)”) + 人 (“person”) + 口 (“mouth (occasionally with the tongue protruding)”) – a person bending over a bottle to drink the alcoholic beverage. The droplets represented drops of the drink or saliva.
In the bronze script, the mouth separated from the body and corrupted into 今 (OC *krɯm), while the rest of the body became 欠 (OC *kʰoms). These two components also acted as phonetic components. These changes were inherited in the seal script, leading Shuowen to interpret this character (㱃) as a phono-semantic compound (形聲, OC *qrɯmʔ, *qrɯms) : phonetic 酓 (OC *qʰɯːm, *qlamʔ, *qlɯːms) + semantic 欠 (“yawn”).
In the clerical script, 酓 has been modified to 食 (“to eat”), which is inherited in the current form.
Etymology 1
From Proto-Sino-Tibetan *ʔam (“to eat; to drink”).
Definitions
飲
- (literary or Cantonese, Hakka) to drink
- (Cantonese) to attend a banquet
- to swallow (tears); to nurse (grievance); to keep in the heart
- Alternative form of 隱/隐 (yǐn, “to hide; to conceal”).
- beverage; drink
- diet; food
- (dialectal Cantonese, including Taishanese, Yangjiang; dialectal Gan; dialectal Hakka; Min) rice water
- (Xiamen, Zhangping, Taiwanese Hokkien) sticky and watery
Synonyms
Compounds
|
|
|
Definitions
飲
- † to give (animals) water to drink; to water (animals)
- (Sichuanese) to water (plants)
- † to wine and dine; to entertain with alcohol and food
Synonyms
Pronunciation
Japanese
| 飲 | |
| 飮 |
Readings
Etymology
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 飲 |
| いん Grade: 3 |
| kan’on |
| Alternative spelling |
|---|
| 飮 (kyūjitai) |
From Middle Chinese 飲 (MC ʔˠiɪmX, ʔˠiɪmH).
The kan'on pronunciation, so likely a later borrowing.
Noun
飲 • (in)